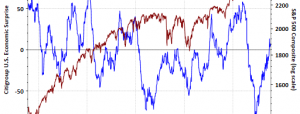
In my bulletin from January 19, 2024, titled “”, I wrote: “The resurgence of inflation will certainly complicate the Fed’s task when it comes to making the decision that markets have been anticipating for several weeks: stock market performance is explained exclusively by the Fed’s promise of a rate cut.”I had also added: “Overall, the market does not seem to be taking on board the risk of supply disruptions in raw materials. Yet this risk is one of the key factors that could radically alter the inflation picture.”Twelve months on, the risk of disruption remains largely absent from valuations, and commodity prices, with a few exceptions, have remained surprisingly depreciated throughout 2024.Agricultural commodities such as coffee, orange juice, chocolate, and eggs have risen spectacularly in recent months, mainly due to factors specific to these markets, such as drought or avian flu. Metals, on the other hand, have not performed remarkably well this year, with investors seemingly ruling out the possibility of short-term shortages.As far as metals are concerned, investors seem to be largely ignoring the risk of shortages… until they become a reality, as was the case in 2024 for germanium, gallium and, more recently, antimony: China has the ability to cause metal prices to fluctuate, if only by deciding to ban exports. As it controls the processing of virtually all metals, it exposes these markets to a significant risk of price spikes, particularly in the context of a trade war. For the time being, this risk remains largely underestimated by the markets. For example, copper closes 2024 at the same level as at the start of the year:(Click on image to enlarge)
China has the ability to cause metal prices to fluctuate, if only by deciding to ban exports. As it controls the processing of virtually all metals, it exposes these markets to a significant risk of price spikes, particularly in the context of a trade war. For the time being, this risk remains largely underestimated by the markets. For example, copper closes 2024 at the same level as at the start of the year:(Click on image to enlarge)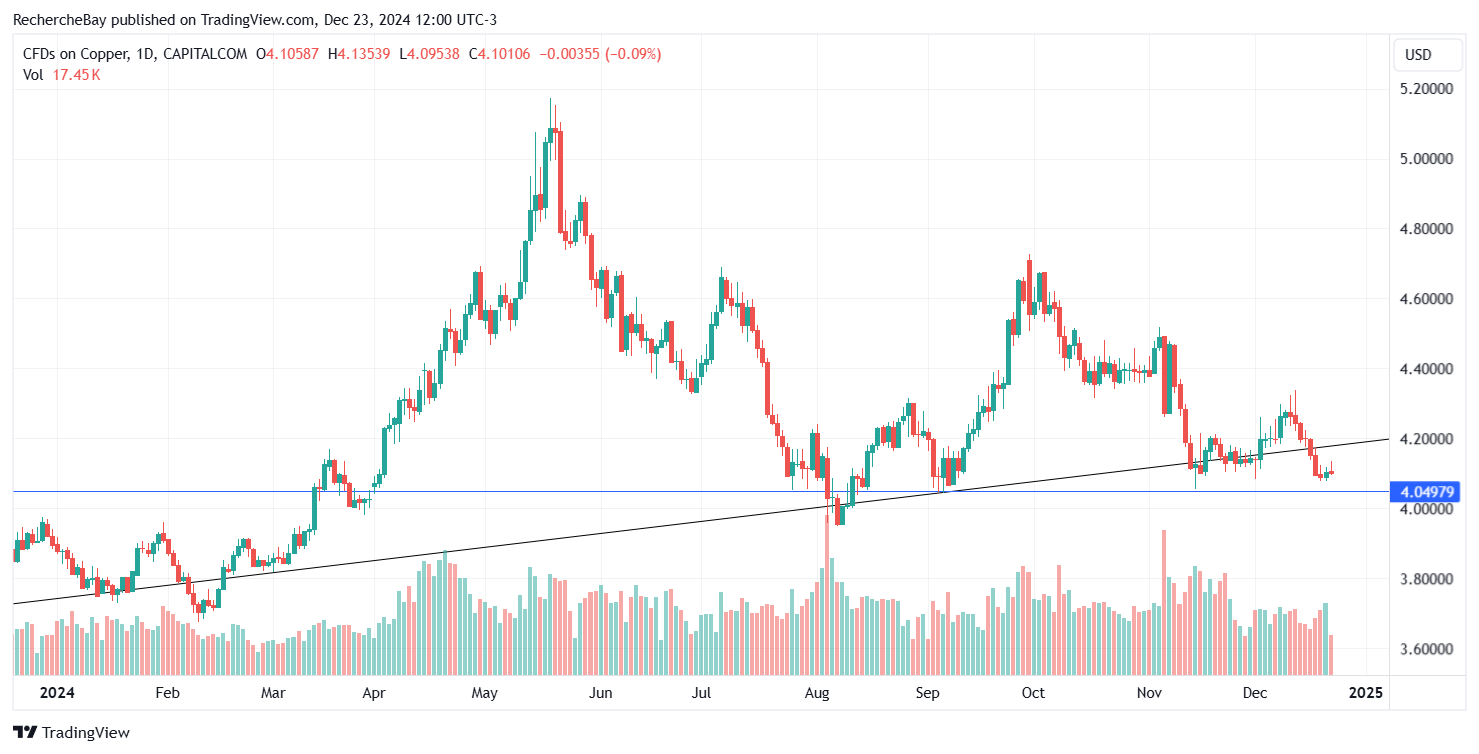 Copper has even lost one dollar since its June highs.Futures sellers are anticipating a sharper-than-expected slowdown in China. These bearish speculators are influenced by the evolution of Chinese bond yields. China’s 1-year yields have collapsed this year, reaching levels comparable to those seen during the great financial crisis of 2008. They have even fallen below the values recorded during the Covid crisis in 2020:
Copper has even lost one dollar since its June highs.Futures sellers are anticipating a sharper-than-expected slowdown in China. These bearish speculators are influenced by the evolution of Chinese bond yields. China’s 1-year yields have collapsed this year, reaching levels comparable to those seen during the great financial crisis of 2008. They have even fallen below the values recorded during the Covid crisis in 2020: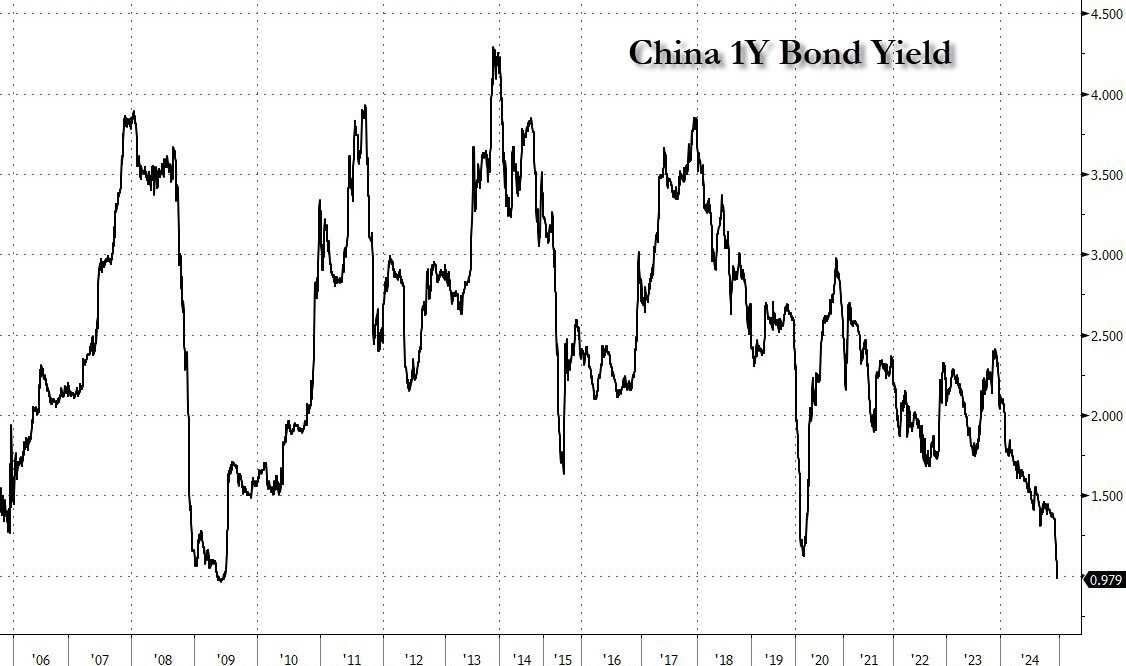 The Chinese 30-year has just fallen below the Japanese 30-year for the very first time:(Click on image to enlarge)
The Chinese 30-year has just fallen below the Japanese 30-year for the very first time:(Click on image to enlarge)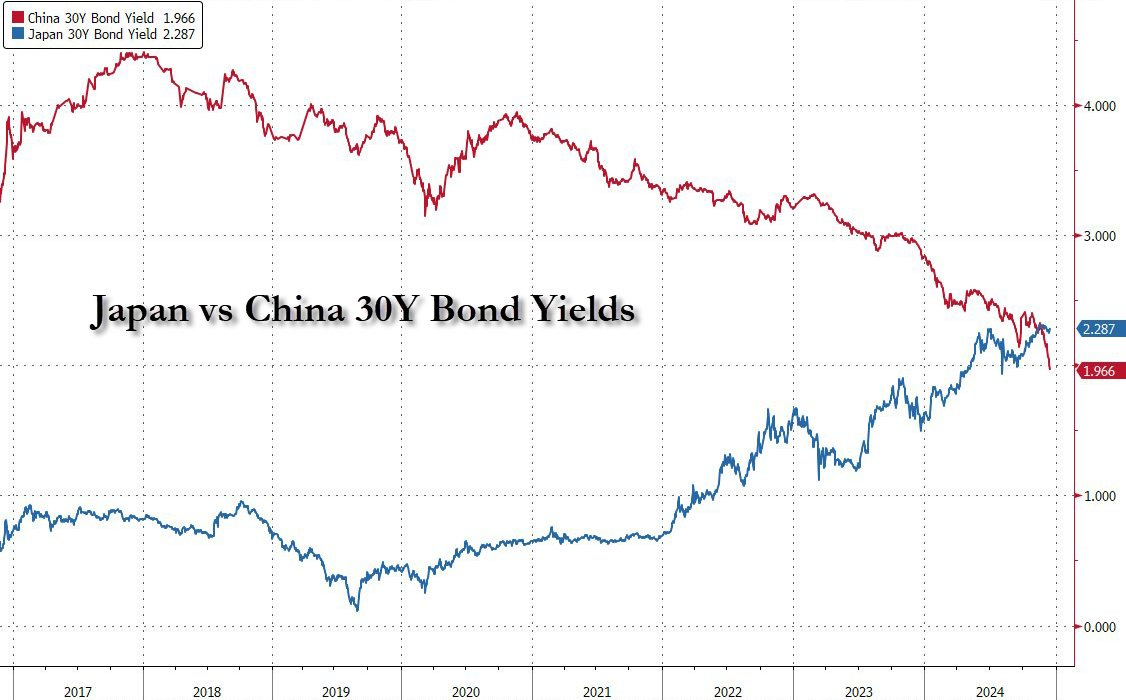 Remember that in 2014, the Chinese 30-year was at 5%:(Click on image to enlarge)
Remember that in 2014, the Chinese 30-year was at 5%:(Click on image to enlarge)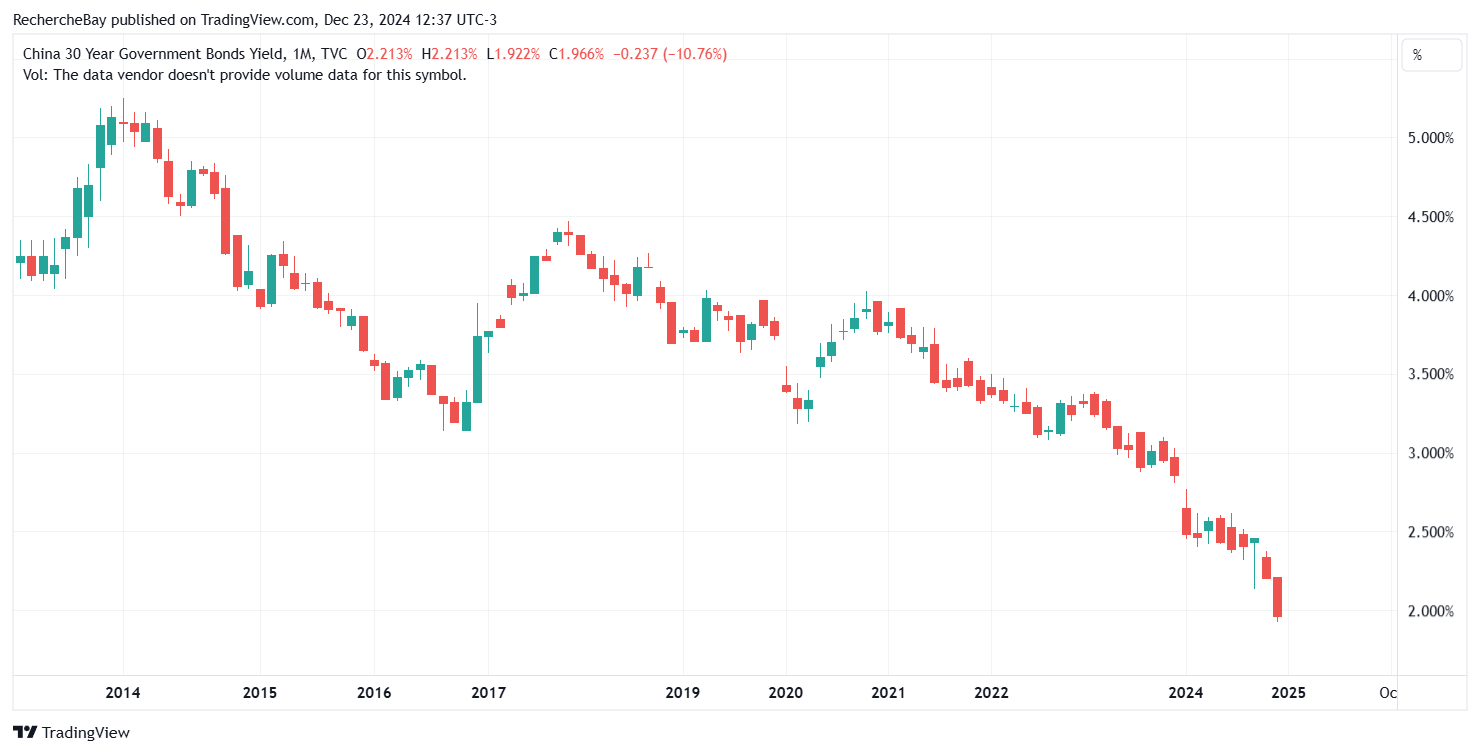 The Japanese 30-year was 0% in 2016:(Click on image to enlarge)
The Japanese 30-year was 0% in 2016:(Click on image to enlarge)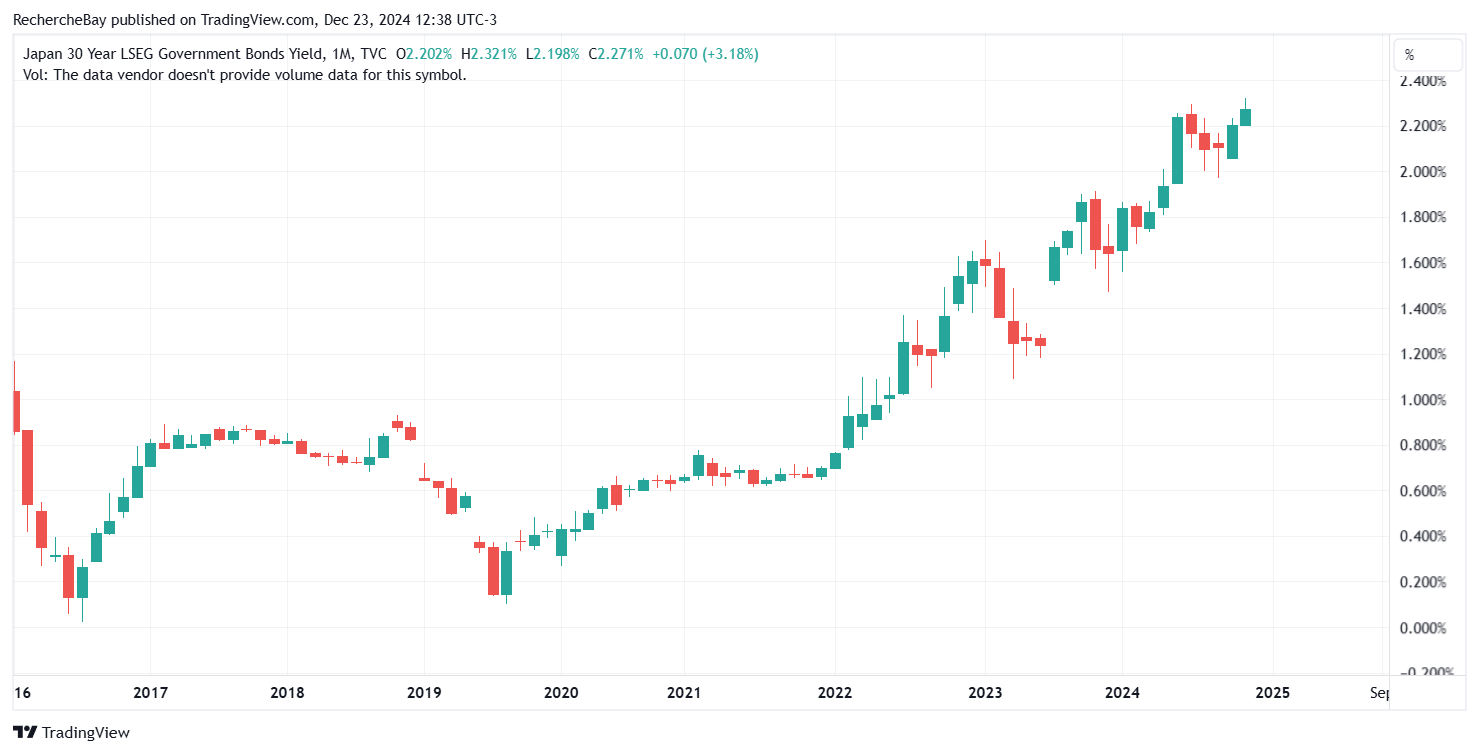 In my bulletin from February 9, 2024 entitled “”, I had written: “The real estate sector accounts for a quarter of China’s GDP, but high levels of leverage suggest that the sector’s deleveraging process could send many banks into a deflationary spiral.According to analyst , who is quite critical of China, there is even a wider systemic risk within the Chinese financial system and economy, associated with the colossal debt of the country’s real estate sector”.As 2024 draws to a close, investors remain convinced that China is following a “Japanization” trajectory, characterized by an imminent demographic collapse and persistent risks in the real estate and banking sectors. These challenges could require a massive “Japanese-style” support package in the years ahead.These concerns about China are probably behind the increase in gold ETF outstandings this year.In my bulletin from April 9, titled “”, I presented this chart of China’s most popular gold ETF:(Click on image to enlarge)
In my bulletin from February 9, 2024 entitled “”, I had written: “The real estate sector accounts for a quarter of China’s GDP, but high levels of leverage suggest that the sector’s deleveraging process could send many banks into a deflationary spiral.According to analyst , who is quite critical of China, there is even a wider systemic risk within the Chinese financial system and economy, associated with the colossal debt of the country’s real estate sector”.As 2024 draws to a close, investors remain convinced that China is following a “Japanization” trajectory, characterized by an imminent demographic collapse and persistent risks in the real estate and banking sectors. These challenges could require a massive “Japanese-style” support package in the years ahead.These concerns about China are probably behind the increase in gold ETF outstandings this year.In my bulletin from April 9, titled “”, I presented this chart of China’s most popular gold ETF:(Click on image to enlarge)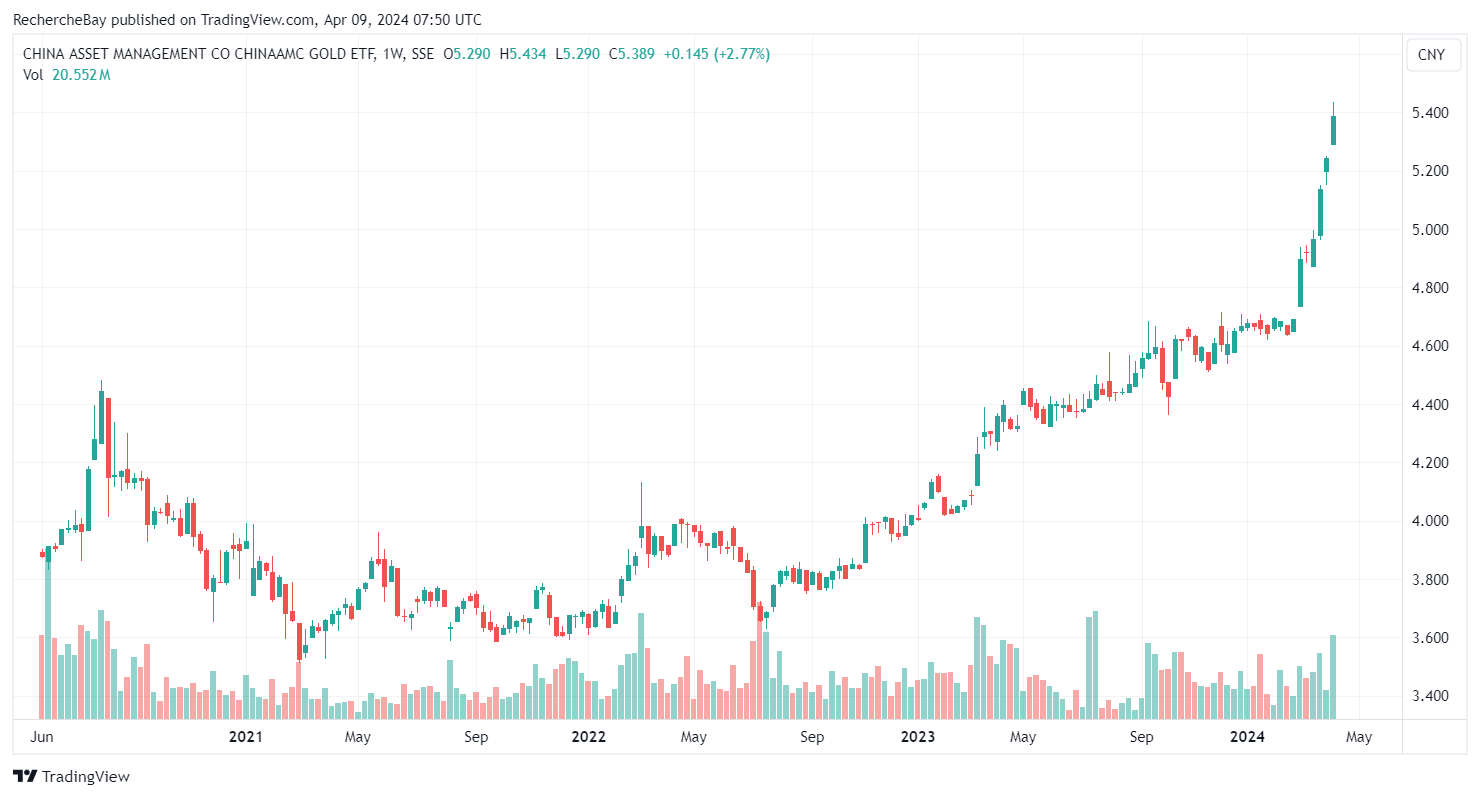 Eight months later, ETF assets under management continue to soar:(Click on image to enlarge)
Eight months later, ETF assets under management continue to soar:(Click on image to enlarge)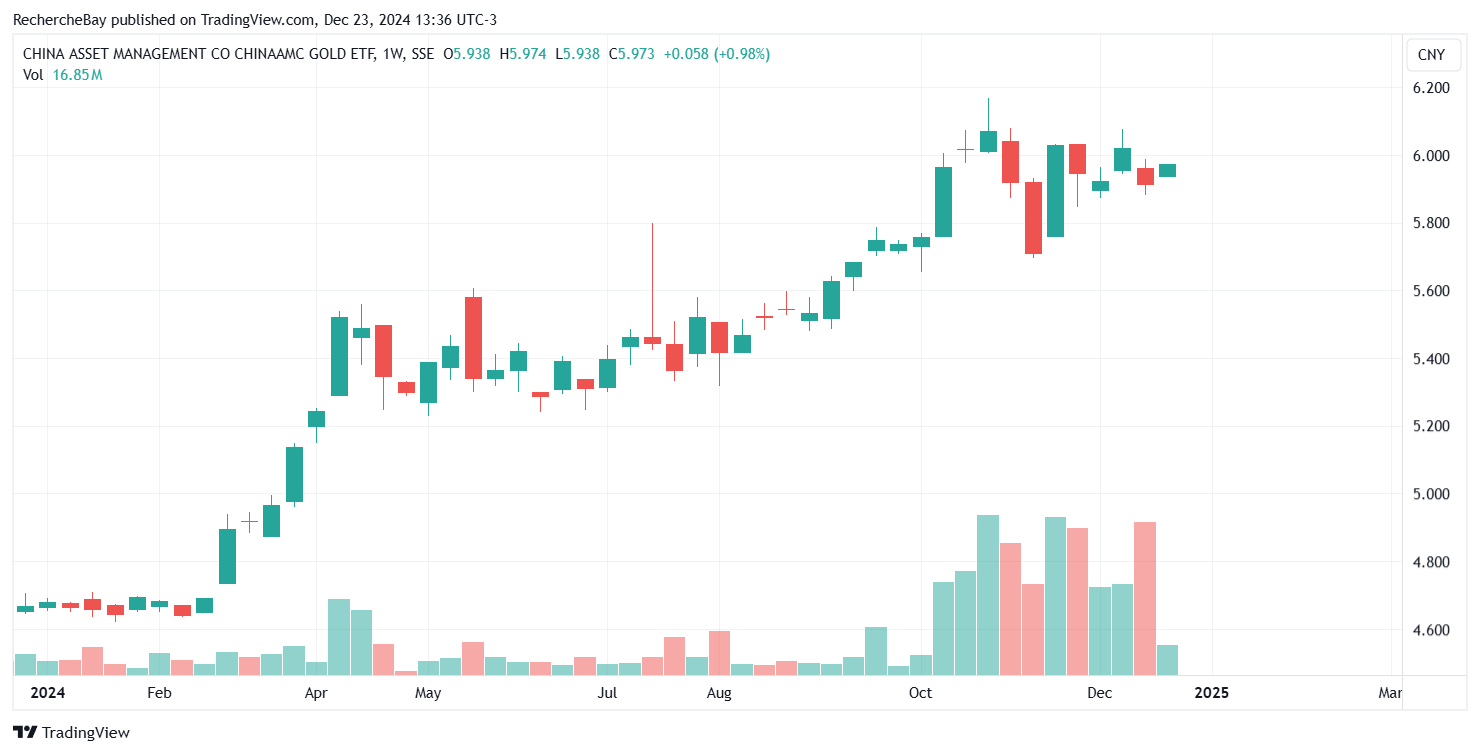 The situation is completely different in the USA, where growth prospects in 2024 have never been in doubt. The strength of the US economy, supported by massive government spending plans and abundant liquidity, has even led to a real awareness of inflation.In early March, Janet Yellen, the US Treasury Secretary, surprised the markets by admitting that .In Europe, inflation in 2024 is all the more worrying as it is accompanied by a marked economic slowdown.In my February 2, 2024 bulletin titled “”, I had written: “Recent rises in inflation have plunged the continent into an unprecedented stalemate: the farmers’ protest movement is mainly attributable to the consequences of this general decline in purchasing power observed in Europe over recent quarters. However, according to Brussels, one of the solutions to counter inflation also involves negotiating free-trade agreements to contain the rise in prices of agricultural raw materials. But these agreements are highly unfavorable to farmers, who have already seen their real wages plummet in 2022 and 2023. The anti-inflationary cure is worse than the disease! In the past, open borders were an effective recipe for containing price rises. However, now that inflation has woken up, this approach no longer works.”Eleven months after the farmers’ revolt in Europe, nothing has been resolved regarding inflation and the causes of soaring energy costs on the continent.Electricity prices in Germany have risen sharply in recent days, reaching levels not seen since the 2022 energy crisis, due to low wind power production. On Wednesday, electricity imports reached their highest level in a decade, forcing gas and oil-fired power plants to step in to meet demand. Prices exceeded €1,000 per megawatt-hour and remain extremely high:
The situation is completely different in the USA, where growth prospects in 2024 have never been in doubt. The strength of the US economy, supported by massive government spending plans and abundant liquidity, has even led to a real awareness of inflation.In early March, Janet Yellen, the US Treasury Secretary, surprised the markets by admitting that .In Europe, inflation in 2024 is all the more worrying as it is accompanied by a marked economic slowdown.In my February 2, 2024 bulletin titled “”, I had written: “Recent rises in inflation have plunged the continent into an unprecedented stalemate: the farmers’ protest movement is mainly attributable to the consequences of this general decline in purchasing power observed in Europe over recent quarters. However, according to Brussels, one of the solutions to counter inflation also involves negotiating free-trade agreements to contain the rise in prices of agricultural raw materials. But these agreements are highly unfavorable to farmers, who have already seen their real wages plummet in 2022 and 2023. The anti-inflationary cure is worse than the disease! In the past, open borders were an effective recipe for containing price rises. However, now that inflation has woken up, this approach no longer works.”Eleven months after the farmers’ revolt in Europe, nothing has been resolved regarding inflation and the causes of soaring energy costs on the continent.Electricity prices in Germany have risen sharply in recent days, reaching levels not seen since the 2022 energy crisis, due to low wind power production. On Wednesday, electricity imports reached their highest level in a decade, forcing gas and oil-fired power plants to step in to meet demand. Prices exceeded €1,000 per megawatt-hour and remain extremely high: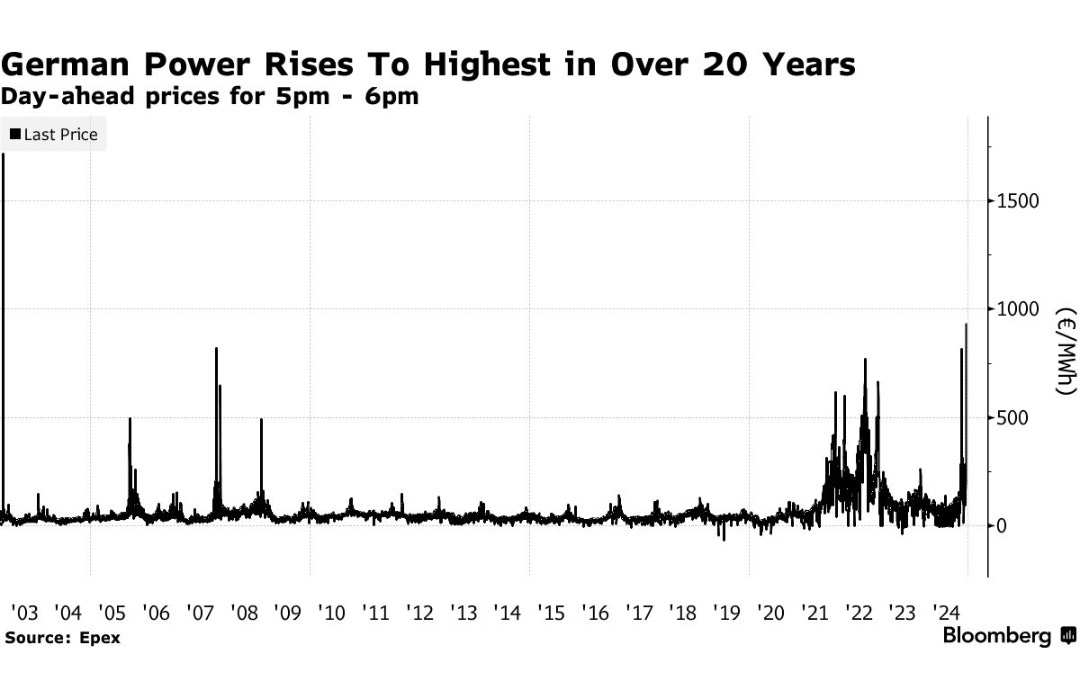 Stagflation is set to take hold in Europe in 2024, but paradoxically, European savers are still very passive in the face of the risk posed by the threat of this coming period of stagflation to the value of bond assets held by savers and to the .In the United States, the risk of inflation also intensified as the year drew to a close. The latest PPI figures confirm this rebound in inflation. Consequently, with inflationary expectations on the rise, it is only logical that 10-year yields should once again soar to new highs. Despite the Fed’s rate cut in September, rates have returned to their highest level since May:(Click on image to enlarge)
Stagflation is set to take hold in Europe in 2024, but paradoxically, European savers are still very passive in the face of the risk posed by the threat of this coming period of stagflation to the value of bond assets held by savers and to the .In the United States, the risk of inflation also intensified as the year drew to a close. The latest PPI figures confirm this rebound in inflation. Consequently, with inflationary expectations on the rise, it is only logical that 10-year yields should once again soar to new highs. Despite the Fed’s rate cut in September, rates have returned to their highest level since May:(Click on image to enlarge)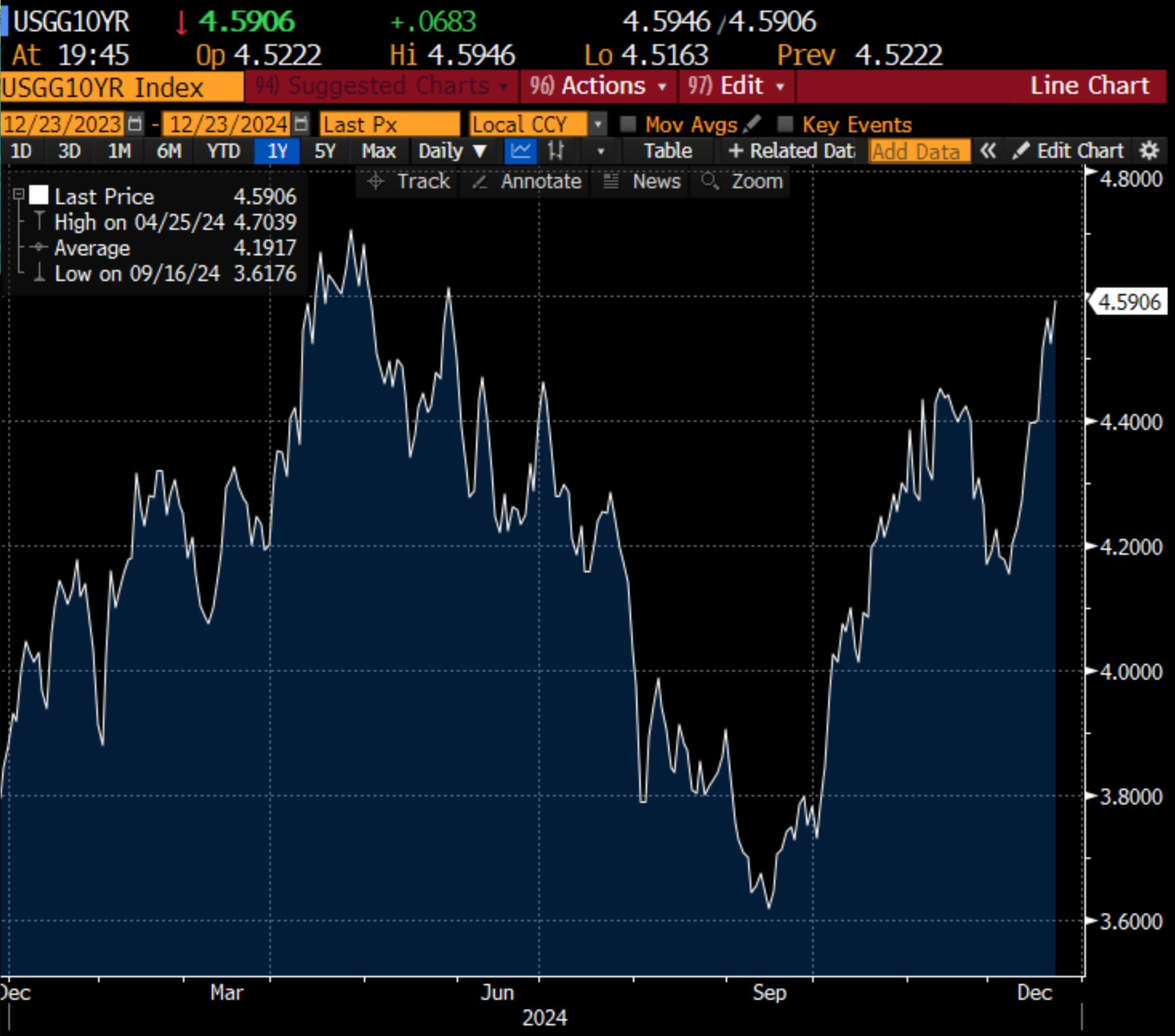 As a direct consequence, the US real estate market is once again under pressure.Last , I said that the real estate market was paralyzed by high interest rates. The situation is deteriorating again: the average 30-year mortgage rate rose sharply to 7.13% after the Fed’s press conference, compared with 6.65% at the same time last year:(Click on image to enlarge)
As a direct consequence, the US real estate market is once again under pressure.Last , I said that the real estate market was paralyzed by high interest rates. The situation is deteriorating again: the average 30-year mortgage rate rose sharply to 7.13% after the Fed’s press conference, compared with 6.65% at the same time last year:(Click on image to enlarge)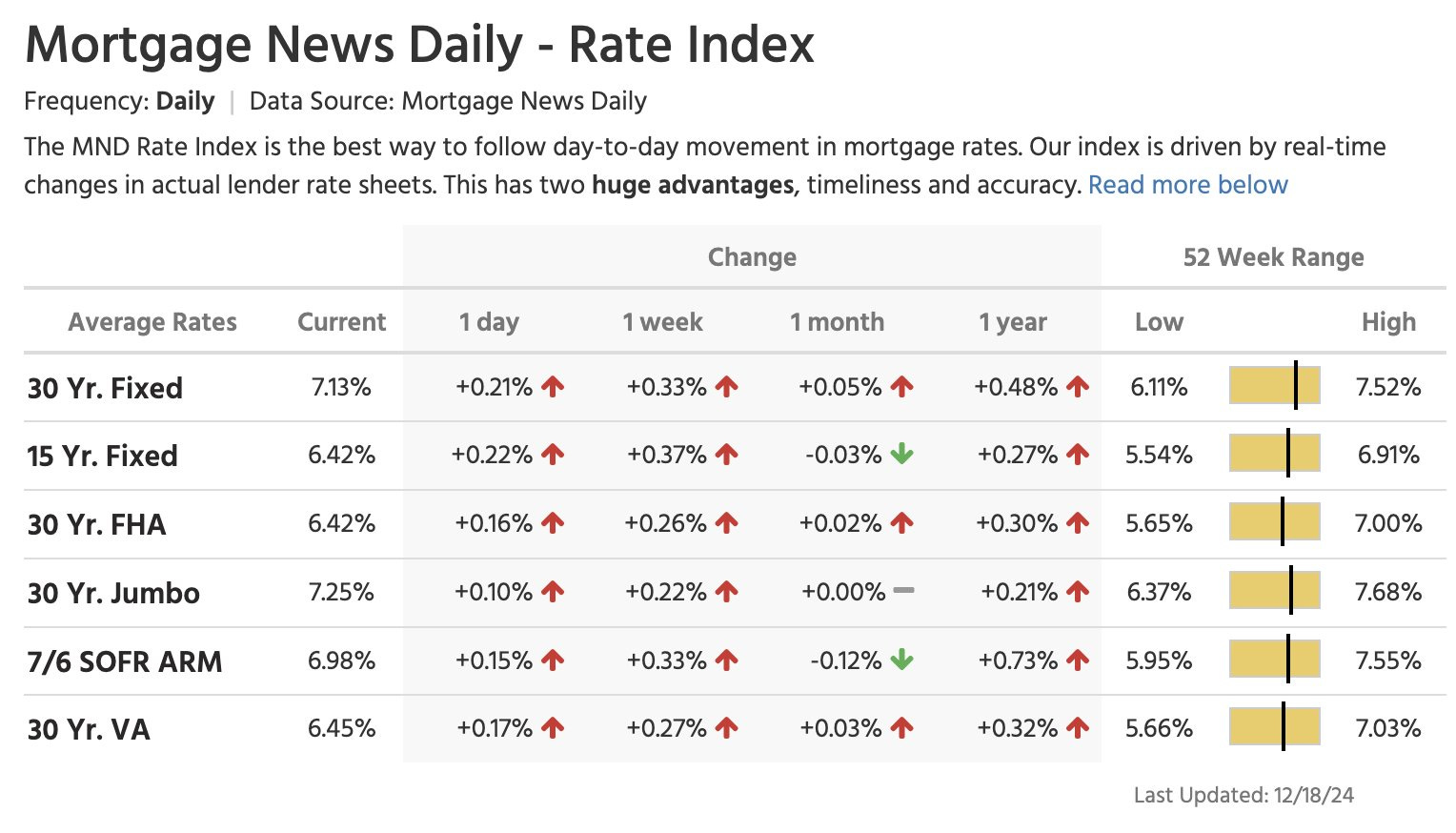 These high rates also represent a huge challenge for short-term refinancing of US debt.This challenge is all the more colossal as the deficit continues to grow at an alarming rate. In the first two months of fiscal 2024, the total deficit reached $380.5 billion, a situation that is already worrying. But over the same period of fiscal 2025, this figure soared to $624.2 billion, a spectacular 64% increase in just one year!(Click on image to enlarge)
These high rates also represent a huge challenge for short-term refinancing of US debt.This challenge is all the more colossal as the deficit continues to grow at an alarming rate. In the first two months of fiscal 2024, the total deficit reached $380.5 billion, a situation that is already worrying. But over the same period of fiscal 2025, this figure soared to $624.2 billion, a spectacular 64% increase in just one year!(Click on image to enlarge)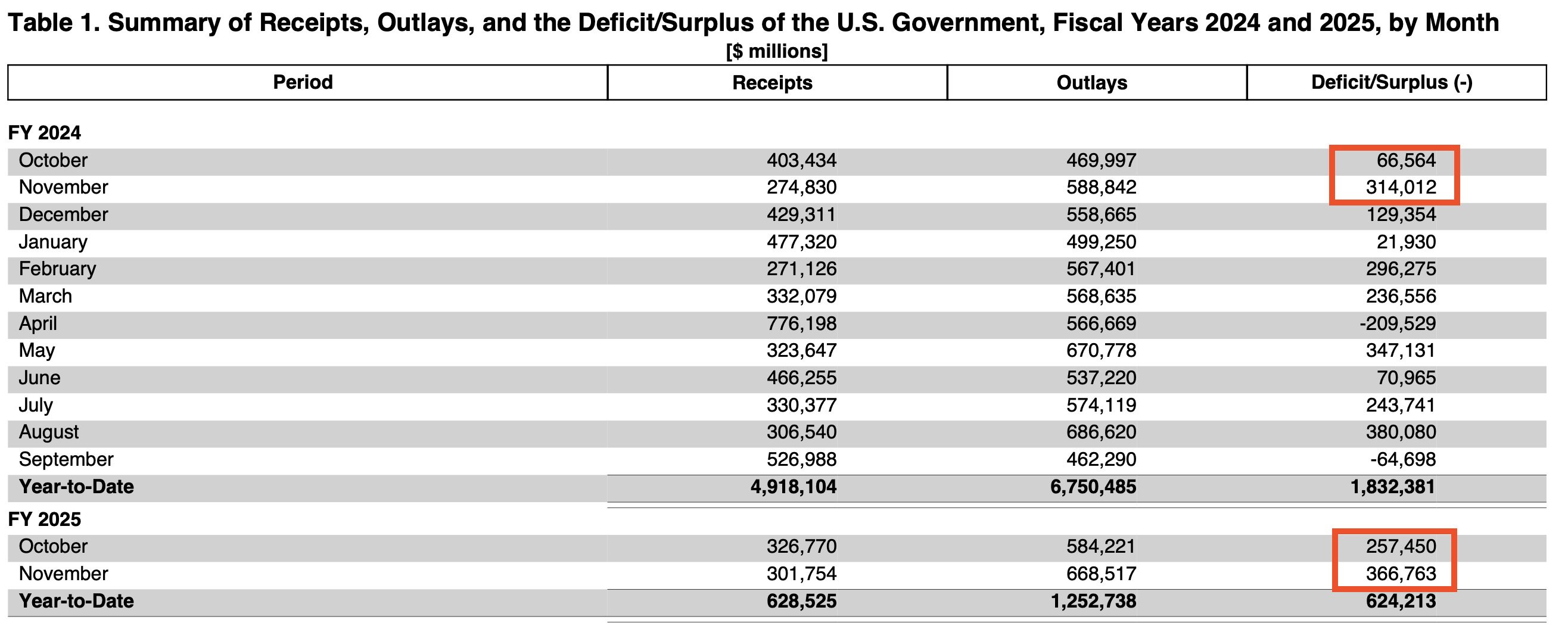 A growing proportion of debt is now financed by short-term bills maturing in less than a year. With $2 trillion in bonds, notes and bills maturing in 2025, plus another $2 trillion in annual budget deficits (and still this figure is likely to be far exceeded), gross financing requirements reach a total of $4 trillion.The need to finance such a large amount of new debt is the main argument in support of the forecast increase of the in 2025.
A growing proportion of debt is now financed by short-term bills maturing in less than a year. With $2 trillion in bonds, notes and bills maturing in 2025, plus another $2 trillion in annual budget deficits (and still this figure is likely to be far exceeded), gross financing requirements reach a total of $4 trillion.The need to finance such a large amount of new debt is the main argument in support of the forecast increase of the in 2025.